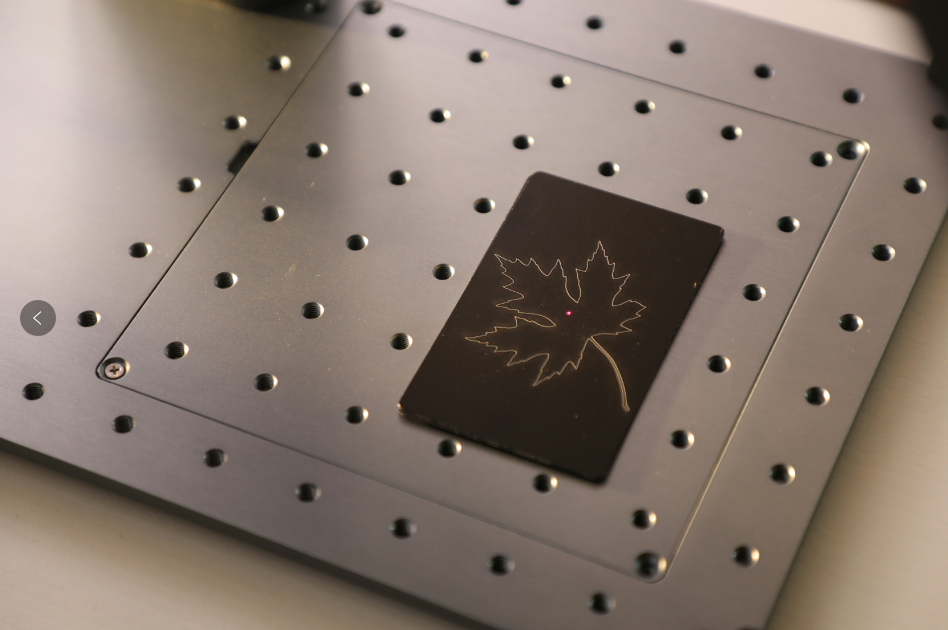
1.Historical Background of Laser Engraving
- The history of laser engraving machines can be traced back to the late 1960s and early 1970s. At that time, laser technology had just been invented and people began to realize its potential applications in the field of material processing.
- In 1960, when Theodore Maiman invented the first working laser, the pioneering stage of laser technology began. In the following years, laser technology has developed rapidly, and the power and stability of lasers have continued to improve.
- By the 1970s, laser technology had begun to be applied in the field of material processing. The earliest laser engraving machines used CO2 lasers, and their working principle was to cut and engrave by focusing the laser beam on the surface of the material.
- With the continuous advancement of technology, the performance of laser engraving machines has been significantly improved. From the initial low-power, low-precision equipment, it has developed into today's high-power, high-precision advanced equipment. Modern laser engraving machines use advanced laser technology, automated control systems, and sophisticated optical components, enabling them to achieve more delicate and complex engraving tasks.
- In addition to CO2 lasers, modern laser engraving machines also widely use other types of lasers, such as solid-state lasers and fiber lasers. These lasers have different characteristics and application advantages, suitable for different types of materials and engraving tasks.
- In general, laser engraving machines have undergone decades of development and evolution and have become one of the indispensable tools in modern manufacturing and art.

2.What is Laser Engraving?
Laser engraving is a process that uses a focused laser beam to remove material from the surface of an object, creating a visible mark or design. The laser beam vaporizes the material, leaving a permanent engraving on the surface. This process can be used on a variety of materials, including metal, wood, plastic, glass, and leather.
3.How Does Laser Engraving Work?
The laser engraving process involves several key components:
- Laser source: The laser source generates a high-intensity beam of light. The most common types of lasers used in engraving are CO2 lasers and fiber lasers.
- Focusing lens: The laser beam is focused through a lens onto the material's surface. The lens determines the size and depth of the engraving.
- Control system: A computer-controlled system directs the laser beam's movement across the material's surface, creating the desired design or pattern. The design is typically created using specialized software and then transferred to the laser engraving machine.
- Material interaction: As the focused laser beam hits the material's surface, it vaporizes a small portion of the material, creating the engraving. The depth and width of the engraving can be controlled by adjusting the laser's power, speed, and focal point.
4.Advantages of Laser Engraving:
- Precision: Laser engraving offers high precision and accuracy, allowing for the creation of intricate designs and fine details.
- Versatility: This process can be used on a wide range of materials, making it suitable for various applications, such as product labeling, personalization, and artistic designs.
- Speed: Laser engraving is a fast process, especially when compared to traditional engraving methods. This makes it ideal for high-volume production.
- Durability: Laser-engraved markings are permanent and resistant to wear, abrasion, and chemicals, ensuring long-lasting results.
- Non-contact process: The laser beam does not physically touch the material during the engraving process, minimizing the risk of damage or contamination.
5.Applications of Laser Engraving:
Laser engraving has numerous applications across various industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Product labeling, serial numbers, and barcodes.
- Personalization: Custom designs on gifts, jewelry, and other personal items.
- Signage: Creating informative and decorative signs for businesses and public spaces.
- Art and crafts: Producing unique designs and patterns on various materials for artistic purposes.
- Medical: Marking surgical instruments and medical devices for identification and traceability.

6.Conclusion:
Laser engraving is a precise, versatile and efficient method for creating permanent marks on a variety of materials. Its ability to quickly and accurately produce high-quality, detailed engravings has made it a popular choice for numerous applications in a variety of industries. As technology advances, laser engraving is expected to continue to play an important role in manufacturing, personalization and art. As a high-performance fiber laser engraver, Lumitool F20 will provide a reliable and efficient solution for your work and projects. Whether you are looking for high-precision production tools in the manufacturing industry or pursuing fine details in artistic creation, Lumitool F20 can meet your needs. If you are interested in our products or have any questions, we are always willing to provide you with more information and demonstrate our technical capabilities.