Click to watch the video:
1.Set the fill parameters
1.1 Set Fill 1 and Fill 2: Vector graphic fill refers to the process of filling the internal area of a vector graphic with color or pattern.
Figure 1: Turning on Fill 1 to show the 30° lines.
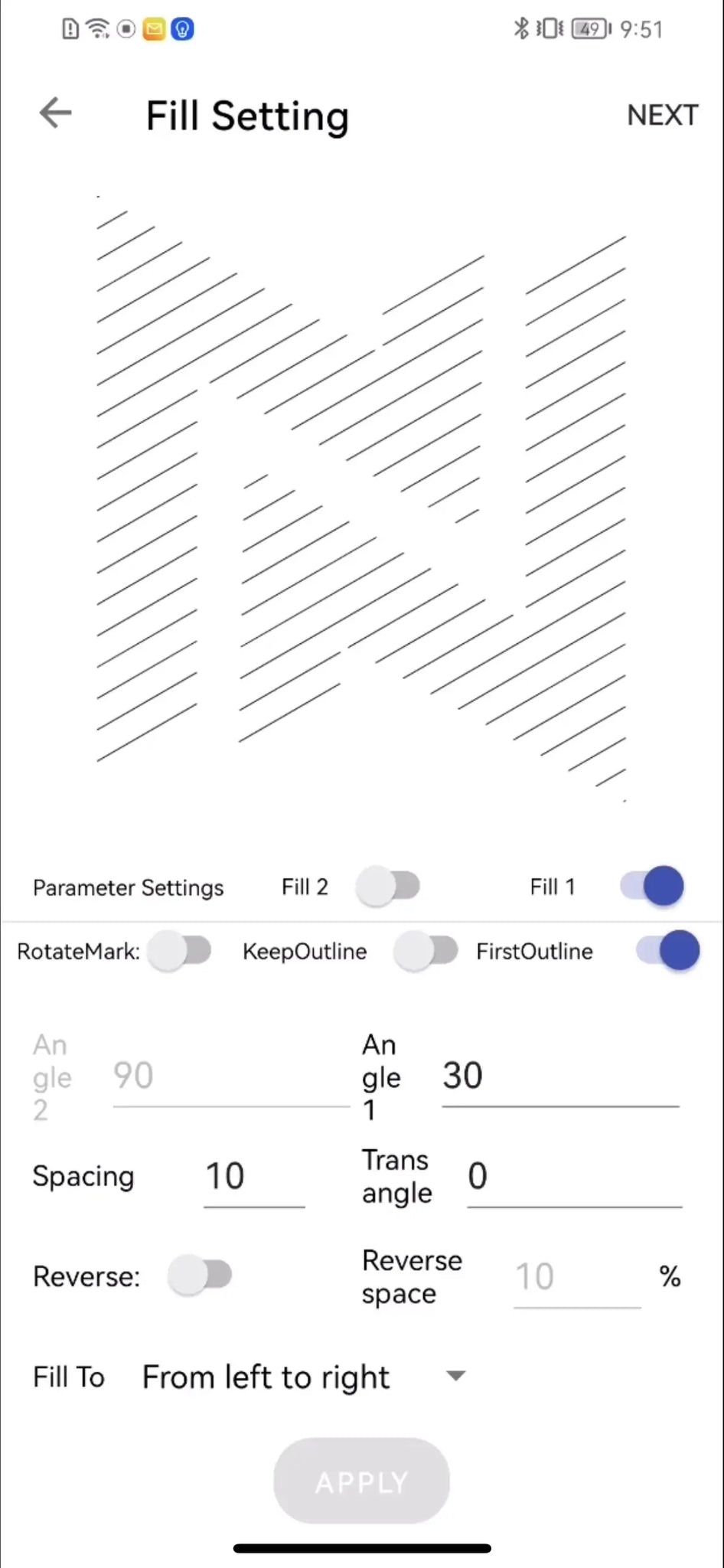


1.2 Fill Spacing and Trans angle



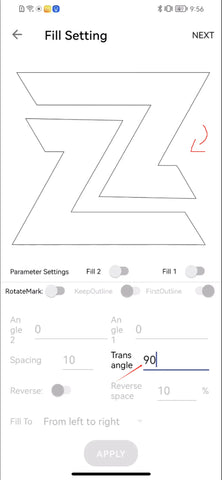
1.3 Reverse and Reverse Space


1.4 KeepOutline 、FirstOutline、Three Fill Directions


2.Printing parameters:
2.1 OffsetX OffsetY



2.2 Width and Height
2.3 Speed and Power
Speed:(See Figure 15)
How fast the marking head moves, in mm.
Fast speed: short marking time, shallow depth.
Slow speed: long marking time, deep depth.
Influencing factors: material type, required depth.

Power:(See Figure 16)
The energy level of laser output.
High power: strong processing capability, deep depth, fast speed.
Low power: suitable for delicate or sensitive materials to prevent excessive ablation.
Influencing factors: material hardness, precision requirements, marking effect.

3.Other parameters:
3.1 On Delay and Off Delay

Off Delay:Default 180 (no need to change)
Off Delay refers to the time delay from when the laser stops receiving the marking signal to when the laser actually stops emitting the laser. This parameter also affects the accuracy of the end position of the marking. Proper adjustment of the off-delay can ensure the accuracy of the end position of the marking and avoid unnecessary additional marking due to too long a delay.
Laser Off Delay:The delay before the laser off.
If the delay is too long: the burn-in effect will be at the end point.
If the delay is too short: the last part of the vector will not be marked.

3.2 Jump Delay and Jump Speed
If the jump delay is too long: no more effect, but the total mark time will be more.
If the jump delay is too short: the mirror will be not stable to the set position, and then the mark will start as following graph.

3.3 Duty Ratio、Area、Frequency、MinPower、External trigger

4.Rotate Parameters:
4.1 RotateMark and Rotate Equipment
4.2 Product Diameter 、Motor Subdivision and Gearspeed
5.Correction Parameters
5.1 Turn XY Turn X Turn Y

5.2 Pincushion、Trapezoid、Paral、Ratio